understanding what we are fightingThe Basic Elements of Fire
The word "fire" refers to the natural phenomenon that occurs whenever a combustible fuel comes into contact with oxygen at an extremely high temperature. Fire is the by product of a chemical reaction in which fuel stored in a combustible fuel, or burnable material at a suitably high temperature (about 617 degrees F, 325 degrees C for wood to burn) is converted to a gas. A fire's flame refers to the visual indication of light that occurs once the gas is heated, and is evidence that a fire has taken place. All fire is essentially the same. In simplest terms, fire is a chemical reaction. |
the fire triangle
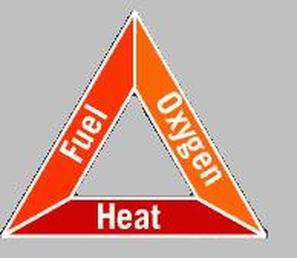
The Fire Triangle was developed by natural scientists as a simple way of understanding the factors of fire. Each side of the triangle represents one of the three ingredients of fire – oxygen, heat, and fuel – demonstrating the interdependence of these ingredients in creating and sustaining fire. Remove any of these three factors from the triangle, and a fire will die.
The interaction of the three equal sides of the fire triangle: heat, fuel and oxygen, are required for the creation and maintenance of any fire. When there is not enough heat generated to sustain the process, when the fuel is exhausted, removed, or isolated, or when oxygen supply is limited, then a side of the triangle is broken and the fire is suppressed.
Heat
A heat source is responsible for the initial ignition of a fire, and heat is also needed to maintain the fire and permit it to spread. Heat allows fire to spread by removing the moisture from nearby fuel, warming surrounding air, and preheating the fuel in its path, enabling it to travel with greater ease.
Fuel
Fuel could be defined as any kind of combustible material, and is characterized by its moisture content, size and shape, quantity, and the arrangement in which it is spread over the landscape. The moisture content of any fuel will determine how easily that fuel will burn.
Oxygen
Air contains about 21% oxygen, and most fires require at least 16% oxygen content to burn. Oxygen supports the chemical processes that occur during a fire. When fuel burns, it reacts with oxygen from the surrounding air releasing heat and generating combustion products (i.e. gases, smoke, particles). This process is known as oxidation.
The interaction of the three equal sides of the fire triangle: heat, fuel and oxygen, are required for the creation and maintenance of any fire. When there is not enough heat generated to sustain the process, when the fuel is exhausted, removed, or isolated, or when oxygen supply is limited, then a side of the triangle is broken and the fire is suppressed.
Heat
A heat source is responsible for the initial ignition of a fire, and heat is also needed to maintain the fire and permit it to spread. Heat allows fire to spread by removing the moisture from nearby fuel, warming surrounding air, and preheating the fuel in its path, enabling it to travel with greater ease.
Fuel
Fuel could be defined as any kind of combustible material, and is characterized by its moisture content, size and shape, quantity, and the arrangement in which it is spread over the landscape. The moisture content of any fuel will determine how easily that fuel will burn.
Oxygen
Air contains about 21% oxygen, and most fires require at least 16% oxygen content to burn. Oxygen supports the chemical processes that occur during a fire. When fuel burns, it reacts with oxygen from the surrounding air releasing heat and generating combustion products (i.e. gases, smoke, particles). This process is known as oxidation.

